Caution
Information in this section refers to a future offering that may not be available at this time. This documentation may also be updated at any time. Please reach out to your Account Manager for more information.
Making Changes¶
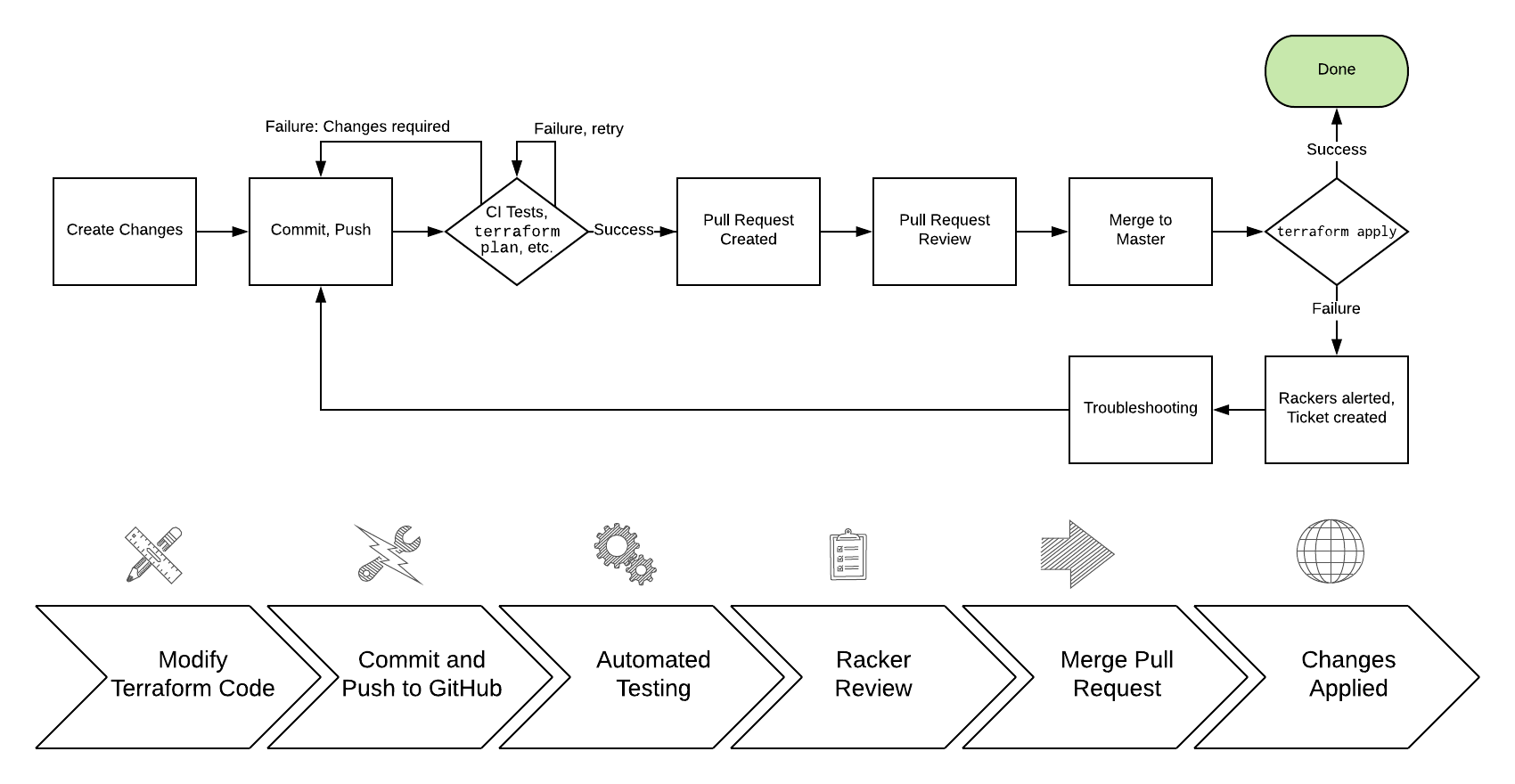
Initiating a change¶
You may begin the change process via a new pull request or by creating ticket; if you choose to make a pull request, Rackers will be alerted to your pull request and may comment or make additional comments within the pull request. Even if you request a change by creating a ticket, a pull request will be created with your changes, which you may review. You must have a GitHub account if you would like to participate in pull requests.
After you’ve made your Terraform changes, committed them using git, and pushed them up to GitHub.com, your repository will automatically begin building the changes. Specifically, changes will be checked against style rules (also known as linting), and a terraform plan will be run for each layer that contains changes. You may create a pull request at any time while these steps are running.
Pull requests are at the heart of making a change in an infrastructure as code world. A GitHub concept, pull requests, “is how you tell others about changes you’ve pushed to a branch in a repository on GitHub. Once a pull request is opened, you can discuss and review the potential changes with collaborators and add follow-up commits before your changes are merged into the base branch.” Detailed review and conversation about changes is encouraged in GitHub.
There are two required checks that must pass for your pull request to be merged:
- Approval (
rackspace/approval): The pull request must be approved by at least one Racker, using the GitHub PR review mechanism. Approvals by the committer will not count towards this requirement. - Plan (
ci/circleci: plan): The branch must successful passterraform fmtand successfully runterraform plan. If either of these steps fail, you may push additional commits to address them.
Approving a change¶
Rackers must approve pull requests, before any changes are merged to the master branch. If you would prefer to approve any changes or pull requests as well, please explicitly state this in a ticket or pull request. If you would also like to have a change deployed on a specific schedule, please note that, too.
When Rackers review a pull request, they are looking to understand:
- Did all automated tests and checks pass? Are the code changes technically correct?
- Does this change do what was requested, in an appropriate and well-designed way?
- Can Rackspace proceed with making the change (now or at a specific time)?
- Does this change require any additional, explicit approval from the requestor?
Deploying a change¶
Changes are deployed when a pull request is merged by you or by Rackspace (adding new commits to the master branch). Using the layers concept described in the Terraform standards in this site, each layer’s terraform plan is repeated, and then terraform apply is run to finish that layer. If Terraform encounters any problems during this process, the entire build of the master branch will be marked failed, and an emergency Rackspace ticket will be created for Rackers to investigate.
Additionally, please consider the following when deploying a change or performing actions on a pull request:
- Any approvals will be dismissed if additional commits are added to the scope of the pull request.
- Only one pull request will be merged to master, and changes applied, at any given time. Attempts to do more than one may fail.
- Any changes that may be staged far in advance may require re-planning or branch updates at the time of the change. Please be sure to inform Rackspace, in a Support ticket, to schedule for a specific change window or maintenance window. Rackspace may require additional time to update an older pull request as part of a scheduled change.
- Rackspace will not automatically deploy changes without Racker interaction or Racker approval, even if two reviewers approve the pull request. Rackspace doesn’t have a default list of changes that can bypass Racker approval.
To raise issues, questions, and changes that aren’t already represented as pull requests, Customers should open a new ticket with Rackspace Support. GitHub’s Issues feature is disabled on all Rackspace-managed repositories.